What is Response Time? For a monitor to be deemed the best or even optimal, it must satisfy a number of criteria. The refresh rate, viewing angle, color reproduction, and response time are the most typical and crucial ones to consider.
Based on these features, the producers market the monitors. However, we have enough intelligence now to recognize that not all alleged qualities are necessary.
Even from their names, you might have inferred how significant the refresh rate, viewing angle, and color reproduction are.
Read More: What is cloud computing? Trends, the future of technology
Explore the Contents
What is Response Time?
Numerous photographs and movies are inputted into computers. These images can be completely white, completely black, or bright like a rainbow, among other color combinations.
Most monitors use red, green, and blue colour filters to produce these hues. As a result, the light from these LEDs is blocked when a darker region of an image is required, while it is permitted to flow for a bright section.
The darker image gradually turns white, although it takes some time. The response time of the display is the length of time it takes for a pixel to change from black to white and back to black. The term for it is “B-to-B response time.”
However, because the LED must completely shut off, then illuminate, before closing once more, the B-to-B response time is quite long. The transition from one shade of grey to the next is timed, despite the fact that the lighting in this scenario isn’t quite incorrect. For example, a monitor panel with a 4 ms GtG reaction time means that the screen’s greyscale color levels are changed every 4 ms.
The majority of colors in photos can be represented in a variety of ways by utilizing greyscale, a combination of black and white and a color filter. As a result, utilizing GtG reaction time, the monitor’s response time may be precisely measured.
Does Response Time Have an Impact on How We View?
Do you now believe that a minor delay in the color change will have an effect on your work? It varies.
What is Response Time? Most monitors respond in less than 10 ms Response time won’t significantly affect how you feel while watching some movies.
The fast changing graphics and scenes in video games and movies can sometimes leave a trail behind when the monitor’s response time is excessive. When the later scene appears, you will notice that the earlier image is still visible above the new scene since the monitor is still changing the colors for the previous image.
The monitor’s refresh rate must be consider. This is because ghosting only occurs when the monitor refreshes the screen more quickly than its response time.
Let’s take a clear look at this. Let’s say you have a display with a 60 Hz refresh rate. One frame will take 16.67 milliseconds to load since one second is equal to 1000 milliseconds. The color change will occur now even if your monitor has a response time of 10 ms before next frame loads on the screen.
However, it will take roughly 6.94 ms for one frame to load on a monitor with a 144 Hz refresh rate. Therefore, to avoid ghosting, the response time must be less than 5 ms.
Overall, high frame rate games and scenes with more color variety, like those in movies, require faster response times. Additionally, if you use a display with a faster refresh rate, it could somewhat spoil your experience.
Having said that, the response time has significantly decreased in recent years—even below 1 ms—thanks to advancements in Nano IPS panels, OLED displays, and monitor overdrive settings. The majority of monitors now offer a reaction time of 5 ms or less. Furthermore, you might not need to stress too much about response times.
Is it the same as latency and input lag?
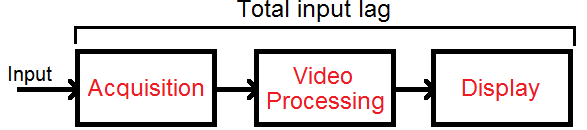
People occasionally refer to input lag and latency as “reaction time” or “response rate” when examining the monitors’ features. People may get uncertain about whether the feature is necessary or not as a result.
Input lag is the amount of time it takes for the result to appear after you give the instruction. Like when you inserted a USB drive into the monitor and loaded an image from it. The input lag is the amount of time it takes from the moment you double-click an image file until the image appears on screen.
The circuitry of the monitor’s circuitry and the pixel response time both contribute to input lag. Similar to that, latency refers to the delay between the system’s and the monitor’s processing of the signal, but not the colors.
However, if the monitor already has latency, it automatically affects. This is due to the latency, which prevents you from seeing the color shift until the image has been processed.