A CMOS Battery’s Lifespan; How long it works?

A CMOS Battery’s Lifespan, In order for the system to remember all of your BIOS configurations even after the machine has turned off, the CMOS battery provides power to the CMOS chip.
The current-voltage of a CMOS battery is one important factor that affects battery longevity. Once it reaches a point where it is unable to provide the CMOS chip with the minimum necessary voltage, the CMOS battery is rendered worthless.
Any data saved on the CMOS chip will be reset to its default value once the battery dies. The system clock and all of your BIOS settings are included in this data. The CMOS battery in your system may need to be replaced if you notice that the BIOS or system clock resets each time you switch it on.
Read More: BIOS store in Computer/Where does computer’s BIOS reside?

A CMOS Battery’s Lifespan, How long is the CMOS battery good for?
Depending on the CMOS battery charge capacity, the system uptime, the motherboard standby current, and numerous other conditions, the CMOS battery can live between three and 10 years.
When a CMOS battery is not in use, its voltage progressively drops. As a result, if you leave your computer off, the CMOS battery will eventually run out because it is always being used by the system. The battery might not survive longer than four years in such a situation.
On the other side, when you turn on the machine, the CMOS battery is not used. Therefore, the CMOS battery could possibly survive up to ten years if you use the computer continually.
What to Look for in a Dying CMOS Battery?
All of your BIOS settings and Real Time Clock are stored on the CMOS chip (RTC). Once the CMOS battery fails, all of these setups will be reset. Even some motherboards have functions that indicate when the CMOS battery needs to be changed. When the CMOS battery runs out, some motherboards even have functions that display a message.
Here are various methods for figuring out if your CMOS battery is dead.
A CMOS Battery’s Lifespan, Inaccurate time and date.
The RTC (Real-time Clock) chip on your motherboard serves as a timekeeper. However, the RTC chip needs steady electricity to operate. The CMOS battery serves as the power source for the RTC while the system is turned off. Additionally, your system time will reset each time you turn off the computer if the CMOS battery is not working.
Your computer time will not be accurate if you have not synchronized it with an internet time server.
You’ll notice that your computer’s time is inaccurate if you haven’t synced it to a time server.

BIOS settings repeatedly reset.
On a CMOS chip, all of your motherboard configurations are stored. These include the XMP of the RAM, the hardware frequency at which it runs, and any other BIOS-configurable parameters.
The CMOS chip, like the RTC chip, stores all of its information as long as it receives consistent power. The CMOS chip draws power from the CMOS battery when the system is turned off.
Your BIOS configurations will all be reset once the system is turned off if the CMOS battery dies. If you have altered the BIOS settings, you will notice this especially clearly. You could have CMOS checksum errors or System battery voltage is low errors in addition to BIOS settings.
A CMOS Battery’s Lifespan, Error Message for POST.
Your system’s motherboard first does a POST when you turn it on. The system inspects important hardware parts during POST. Any data mismatch in the CMOS chip is also found by POST. These CMOS chip defects could be a sign of a failing CMOS battery.
Verify for Any Visible Damage.
You can examine your CMOS battery physically for damage. The CMOS battery is housed in a specific slot on your motherboard. A dead battery may be indicated by any outward signs of damage to the CMOS battery. A bloated or oxidized battery may be the source of these issues.
Verify CMOS Battery Voltage.
A CMOS Battery’s Lifespan, If you want exact information, you can use a voltmeter to check the CMOS battery’s voltage.
It need not reach 0 voltage to lose all usefulness. Your CMOS chip’s minimum operating voltage may change depending on the type of chip you have.
- Set the multimeter to read voltage from a DC source and turn it on.
- Place the red lead against the CMOS battery’s side. Afterward, touch the black lead to the CMOS battery’s opposite side. The reading should appear on the display panel of the voltmeter.
How Should I Proceed If the CMOS Battery Is Dead?
The first thing to do is swap out the CMOS battery after you’re positive that it’s dead.
You must first gain access to the motherboard in order to remove the CMOS battery because the CMOS battery slot is built within the motherboard.
A CMOS Battery’s Lifespan, Delete the PC side panel.
- Unplug the PSU from any wall outlet while turning off your computer.
- To release the capacitors’ remaining charge, briefly press the power button.
- To remove the side panel from the CPU case, unscrew every screw on that side.
Find CMOS Battery.
The motherboard is connected to the CMOS battery. The motherboard of desktop PCs has a unique circular slot that is used to house the CMOS battery. As for laptops, their motherboards might include a dedicated slot, exactly like those of desktop PCs.
If the motherboard of the laptop lacks a dedicated slot, a brief cable should be used to link the CMOS to one of the ports. The CMOS battery will then be covered in electrical tape.
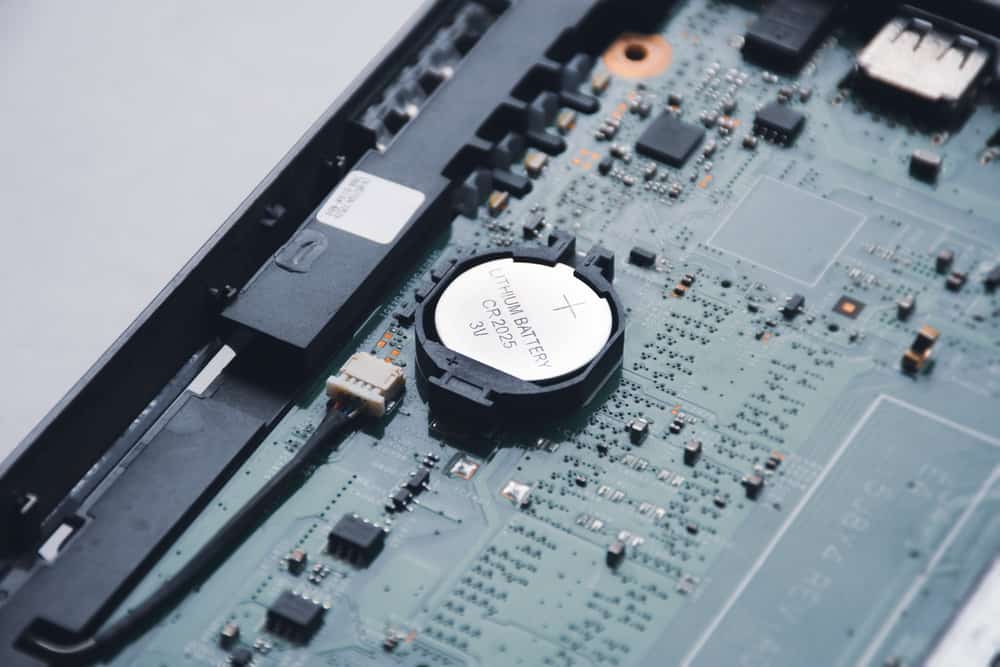

A CMOS Battery’s Lifespan, Change the CMOS battery.
- To remove the CMOS battery from the socket, depress the latch holding it in place.
- Place the brand-new CMOS battery in the motherboard’s CMOS battery slot. Make sure the battery is inserted with the + sign facing up.
- Place the side panel in place and secure all of the previously removed screws.
- After assembling everything, start your system.
How Can I Extend the Life of My CMOS Battery?
If not used for a prolonged period of time, the CMOS battery loses the charge it has stored inside. When this occurs, the battery is unable to supply the CMOS chip with the minimal voltage needed.
The system does not use the CMOS battery while it is continuously turned on. Therefore, we advise that you use your computer frequently if you want to lengthen the life of a CMOS battery.











3 Comments